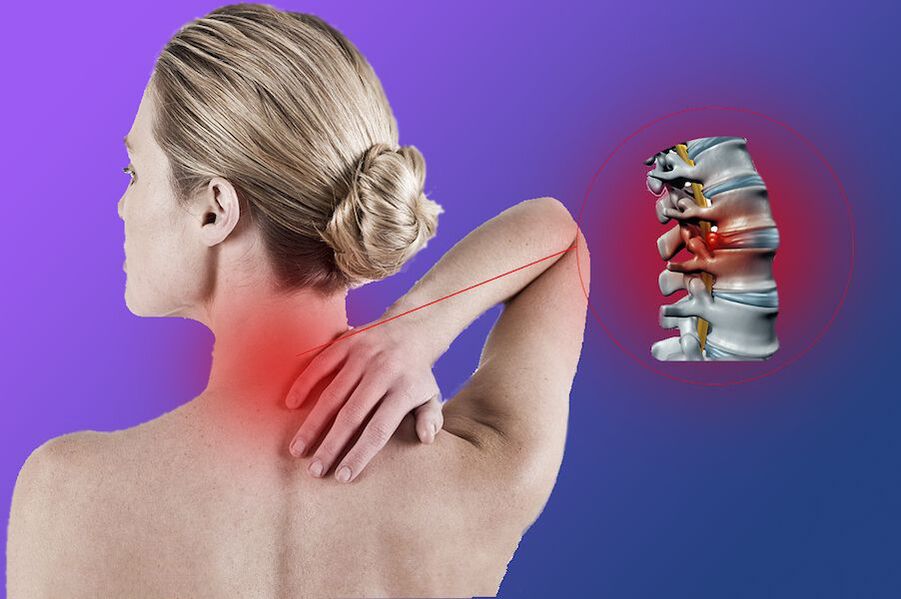
Cervical osteochondrosis is a complex of degenerative disorders that cause damage to the intervertebral discs in the upper part of the spine, changes in their tissue and function. More often, the discs at the level of the fifth, sixth and seventh vertebrae undergo degenerative changes, because this area of the spine is more mobile, it is most involved in head movement, that is, it experiences high loads. As a result of the disease, thinning of the intervertebral discs, disruption of blood supply to the spine, compression of nerve roots, causes pain.
People of any age can suffer from osteochondrosis, but more often the disease occurs in the age group of 30-50 years. Before the appearance of the first attacks of pain, the effects of cervical osteochondrosis are hardly noticeable - anxiety and some heaviness in the neck, dizziness, dimming of the stars in front of the eyes. Often people do not know the real cause of these diseases. However, the sooner the diagnosis is made and the competent treatment is started, the better the chances of a full recovery. Timely treatment of cervical osteochondrosis will help to restore health and give health in the future.
Signs, symptoms and treatment of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis has its own characteristics due to the structure and size of the vertebrae - they are much smaller than the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, but also less durable. Due to the poor development of the neck muscles, the vertebrae experience increased stress and are more likely to be injured.
Regardless of the level of development of modern medicine, the pathogenesis of this disease is not fully understood. Changes in the structure of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs are caused by metabolic disorders in the body, sedentary lifestyle, poor posture and curvature of the spine, overweight, infectious diseases, hypothermia, stressful situations, improper exercise and injuries.
Stages of disease development
- With first-degree cervical osteochondrosis, the pain is still insignificant. During this period, there is discomfort in the neck after long-term tension and tension in the muscle ligaments. All this can be corrected by physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy procedures, ointments and vitamin complexes.
- With secondary osteochondrosis, the pain is exacerbated when nerve endings are compressed and disc protrusions are visible, especially when a person is standing. Periodic dizziness and darkening of the eyes. In addition to physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are also needed.
- The third degree is not paroxysmal, but is characterized by constant pain, spreading to the shoulder area and upper extremities. The appearance of hernias can lead to numbness of the muscles of the hands and a temporary loss of sensitivity of the fingers, impaired mobility of the joints. In some cases, surgery is required in the third degree of the disease.
- Pain decreases with fourth-degree cervical osteochondrosis, but this is not the beginning of recovery. In this case, the intervertebral disc is almost completely destroyed, and osteophytes grow in the joints of the vertebrae, which damage the vertebrae and nerve branches. Brain nutrition deteriorates, resulting in dizziness, tinnitus, decreased vision, and impaired coordination of movements.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Symptoms of osteochondrosis can vary depending on which segment of the spine is damaged and the degree of damage. Most people feel pain in the neck, above (up to the chin) and vice versa, below - in the shoulder girdle, arms, chest. There may be numbness of the fingertips and tongue, general weakness, increased pressure, decreased vision and hearing, and wheezing while moving the neck.
The typical symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- Root Syndrome. When the nerve is constricted, the pain spreads from the neck to the shoulder, spreads to the wrists, hands, and fingers, and swelling appears. The firmness and elasticity of the skin deteriorates, it becomes pale due to poor blood supply.
- Vertebral artery syndrome manifests itself with pain in the back of the head, in the crown, affecting the temporal lobes of the head and superciliar regions. If the head is restless for a long time, for example, pain may increase in trucks that have to constantly monitor the road while driving. Perhaps nausea, dizziness, impaired vision and hearing, vestibular dysfunction.
- Cervical migraine syndrome occurs when the branches of the sympathetic nodes are irritated. When exposed to nodules, there is a disruption of cerebral vessels, deterioration of blood supply to tissues. The patient experiences increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, noise in the head, congestion and ringing in the ears.
- Hypertensive syndrome is characterized by an increase in intracranial pressure. The patient feels headaches exploding from the inside, there may be nausea, vomiting, body temperature rises, ESR rises.
Why is osteochondrosis dangerous?
The sooner treatment for cervical osteochondrosis begins, the more likely it is to stop developing and recover. In advanced cases, when irreversible processes occur, treatment will only help relieve pain and inflammation. What is dangerous osteochondrosis and what diseases can cause it:
- protrusions and intervertebral hernias;
- vertebrogenic cervicalgia (limited neck mobility);
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- migraines and severe headaches that do not go away even after taking modern painkillers;
- impaired vision and hearing;
- paresis;
- formation of osteophytes;
- deterioration of blood supply to the brain and more.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can be effective only if it is comprehensive and includes:
- drug treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra aimed at reducing pain and inflammation;
- physiotherapy procedures;
- medical gymnastics;
- manual therapy methods;
- In extreme cases, when conservative treatment does not help and the patient's condition worsens or paralysis of the limbs occurs, surgery is performed.
Determining the causes of cervical osteochondrosis with certain symptoms and treatment is not a quick process. Depending on the patient's immunity, body condition and stage of the disease, the course of intensive care can last from 1 to 3 months, followed by maintenance procedures for about a year.
Medical therapy
Drug treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine is aimed at:
- reduction of pain;
- elimination of inflammation;
- get rid of swelling;
- improved metabolism;
- cessation of degenerative processes and tissue regeneration.
At present, drugs that can cope with all the tasks at once have not yet been developed, so the doctor may prescribe several drugs at the same time.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are among the drugs used to relieve pain and inflammation in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Antispasmodics help relieve spasms and reduce pain. Non-steroidal ointments and topical gels also help to cope with the pain. Diuretics are prescribed to reduce swelling.
In the treatment of cervical and brachial osteochondrosis, it is necessary to use drugs that improve the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, stimulate metabolism and tissue regeneration, and prevent irreversible changes in the joints. These agents include chondroprotectors, vitamins C and B.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine
Physiotherapeutic procedures have a local effect on the affected area, improve blood microcirculation, eliminate swelling, inflammation, relieve pain. Depending on the course of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the following:
- exposure to low frequency currents and electrophoresis;
- massage, including hydromassage (especially useful during recovery);
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound treatment,
- therapy with "soft" laser beams.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is not used in all stages of osteochondrosis and not for all patients, so a qualified specialist should prescribe and implement treatment. For example, its implementation is prohibited in infectious diseases, benign and malignant tumors, blood diseases and intervertebral hernias. What are the positive effects of this method of therapy? After proper treatment, the signs and symptoms of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, such as pain, numbness of the hands, dizziness and tinnitus, disappear. The manipulations relieve tension in the neck muscles, improve blood circulation and strengthen the immune system.
Home treatment of the disease
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis at home is quite acceptable and can be no less effective than in the hospital, but a specialist should prescribe it and follow the course.
It is convenient to perform a number of physical therapy exercises in a comfortable home environment. Gymnastics will help strengthen the neck muscles, improve blood circulation and therefore nutrition of the vertebrae and reduce pain. The main thing in home treatment is systematic procedures. All exercises should be performed smoothly, avoid sudden movements, and gradually increase the load and intensity of training. If the situation worsens during gymnastics, if the pain intensifies, it is necessary to reduce the speed of the lesson and the range of motion.
Folk remedies for osteochondrosis
Traditional medicine also offers solutions in the treatment of cervical and brachial osteochondrosis: the use of infusions and decoctions, therapeutic baths, lubrication with oils, home-made ointments and rubs.
- To reduce pain and eliminate inflammation, take a horseradish leaf before going to bed at night, steam it in boiling water for a few minutes, cool it a bit, then glue it on the inside and wrap it with a warm scarf. Leave the night. Cabbage leaves are also suitable for therapeutic compresses, not only do not evaporate before application, but are lightly beaten with a kitchen hammer.
- Apply honey-potato compress once a week to relieve unpleasant symptoms and treat cervical osteochondrosis. Grate 2 potatoes, add ½ teaspoon. honey, mix well. Apply the resulting cuttings to the damaged area for one and a half to two hours, wrap your neck and try to lie down without moving. Then the gruel is washed with warm water.
- Rubbing to treat osteochondrosis of the neck and relieve symptoms: ½ Take a glass of maple and 2 glasses of alcohol, leave for a week in a well-closed bowl in a dark place. Rub the resulting product on the cervical-collar area.
- Decoction of elecampane roots is used to prepare anti-inflammatory compresses. 2 tablespoons biennial elecampane roots Pour 1 cup boiling water, boil for 10 minutes, then cool and strain. Apply warm decoction compresses to the neck twice a day (morning and evening) and leave on for about 20 minutes. It is also useful to take a bath with the decoction of Elecampane (to take a bath, you need to prepare a decoction of 10 tablespoons of the plant).
- An ointment from hop cones is a less effective tool in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis to reduce inflammation, eliminate the causes and symptoms. To prepare it, take 1 tbsp. ground hop cones, rub well with 1 tbsp. butter or lard. Lubricate the affected area with the resulting product, then cover with a napkin and wrap with a warm scarf. Daily use of the ointment will quickly give the desired result.
Laser treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
At home, you can not only take medication prescribed by a doctor and perform a series of exercises, but also continue treatment with physiotherapy, such as paraffin bandages or laser beams. A unique portable laser device has been developed for the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Its action is effective both in the acute phase of the disease and in remission. Treatment of osteochondrosis with "soft" laser beams will quickly relieve neck pain, reduce inflammation, swelling and improve overall well-being. To achieve the effect, it is necessary to move along the lines along the damaged vertebrae 2-4 times a day for 18-24 minutes, and then move from the vertebrae to the base of the ear.


















